Architecture
Overview
This document provides a high-level overview of the architecture for our Large Language Model (LLM) application, designed to assist back-office employees with intelligent query responses. The application leverages a combination of a large language model (LLM), document embedding, semantic search, and caching to deliver fast and accurate answers based on company documents. Each component is containerized, enabling scalability, modularity, and ease of deployment.
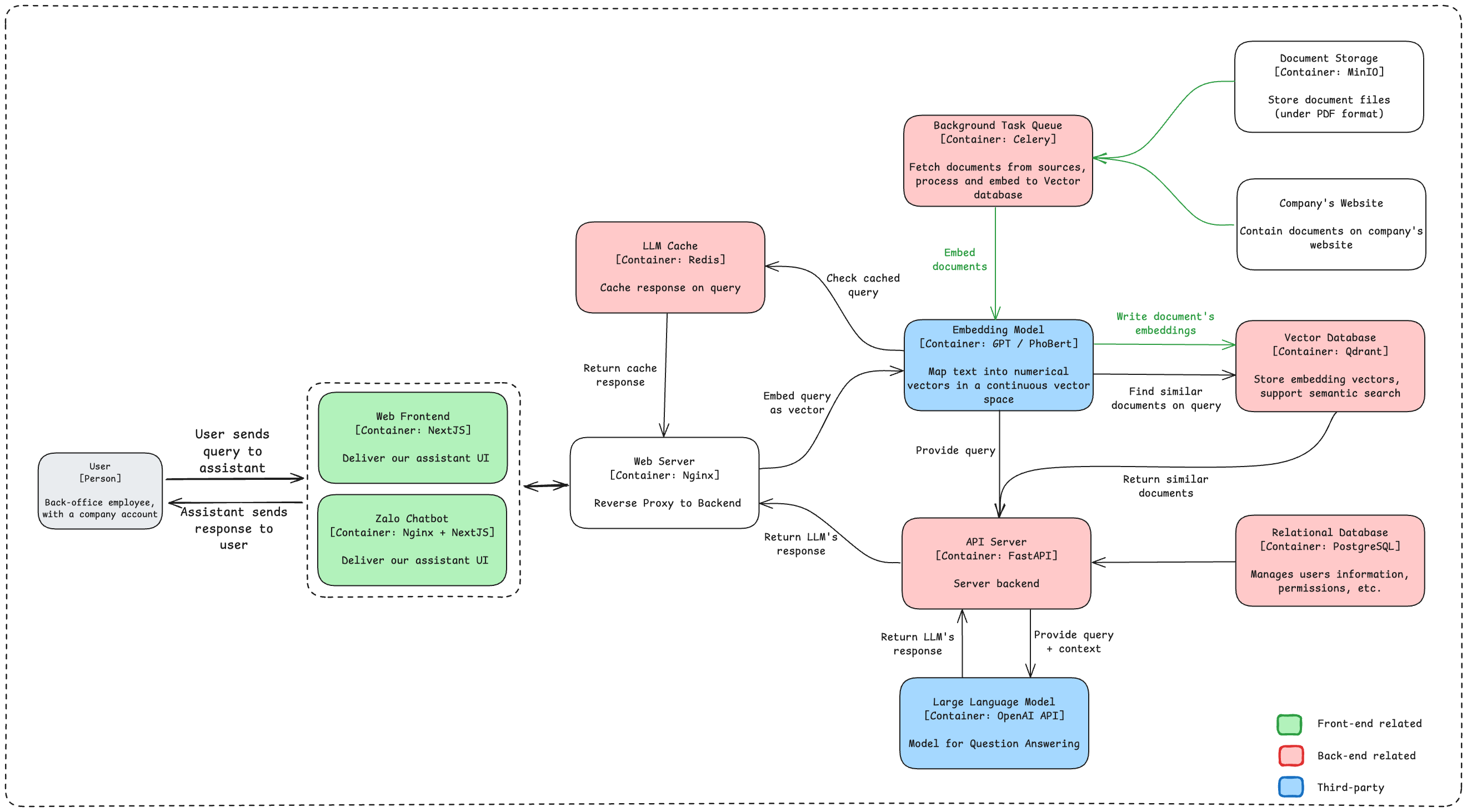
Architecture Diagram
The following is a simplified view of the system’s core components and their interactions:
- User Interface layer
- API & Backend layer
- LLM & Embedding layer
- Data Management layer
- Document processing layer
Components
1. User Interface layer
Web Frontend
- Service: NextJS
- Function: Provides the primary user interface for employees to interact with the assistant. Built with NextJS, the frontend is responsive and optimized for delivering a seamless user experience.
Zalo Chatbot
- Service: using Zalo API
- Function: Acts as an additional chatbot interface, potentially integrated with Zalo (a popular chat platform). The chatbot is proxied through Nginx for better performance and security.
2. API & Backend layer
Web Server
- Service: Nginx
- Function: Operates as a reverse proxy, routing requests from the frontend to the backend API server. Nginx enhances security and load balancing, helping manage high request volumes effectively.
API Server
- Service: FastAPI
- Function: The core backend server, handling API requests, managing cache checks, interfacing with the LLM, and orchestrating document retrieval. FastAPI’s asynchronous capabilities allow the API to handle multiple requests efficiently, making it suitable for real-time applications.
3. LLM & Embedding layer
Large language model
- Service: OpenAI API/self-host LLM model
- Function: The primary LLM for answering user queries. The model receives user queries (with context provided from relevant documents) and generates human-like responses.
Embedding model
- Service: OpenAI API/self-host embedding model
- Function: Maps text to vector embeddings, a process crucial for similarity search. This component enables the system to find and rank relevant documents based on user queries. The choice of GPT or PhoBERT allows flexibility in handling multilingual or domain-specific embedding needs.
4. Data Management layer
LLM Cache
- Service: Redis
- Function: Caches responses from the LLM based on query embeddings, minimizing redundant API calls. This significantly reduces response latency for frequently asked questions and optimizes API usage costs.
Vector Database
- Service: Qdrant
- Function: Stores vector embeddings generated from documents and supports semantic search. When a query is received, Qdrant enables the system to quickly find and return similar documents based on vector similarity.
Relational Database
- Service: PostgreSQL
- Function: Manages structured data, including user information, permissions, and system metadata. This database is essential for tracking user access and managing query history and other operational data.
5. Document Processing layer
Document Storage
- Service: MinIO
- Function: Stores documents (in PDF format) sourced from the company’s website or other repositories. MinIO, an S3-compatible object storage solution, offers scalable and private storage for company documents.
Background Task Queue
- Service: Celery
- Function: Orchestrates background tasks, including document fetching, processing, and embedding. This allows the system to handle these tasks asynchronously, ensuring that document indexing does not impact the main query processing flow.
Workflow
- User Query:
- A user submits a query through the Web Frontend or Zalo Chatbot.
- Request Handling:
- The query is routed via the Web Server (Nginx) to the API Server (FastAPI).
- Cache Lookup:
- The API Server checks the LLM Cache (Redis) to see if a response for this query is available.
- If a cached response is found, it is returned to the user, reducing latency and API costs.
- Embedding and Document Retrieval:
- If no cache hit, the query is embedded by the Embedding Model and sent to the Vector Database (Qdrant).
- Qdrant performs a similarity search, returning relevant documents.
- LLM Query:
- The API Server forwards the user’s query and relevant document context to the Large Language Model (OpenAI API) for response generation.
- The response is then cached in Redis for future use.
- Background Document Processing:
- Periodically, Celery fetches new documents from the Company’s Website, processes them into vector embeddings using the Embedding Model, and stores these embeddings in the Vector Database for future query matching.
Acknowledgements
This application builds on top of other open-source projects and leverages them:
- NextJS for a dynamic and responsive front-end.
- FastAPI for a high-performance, asynchronous API backend.
- Redis for caching responses and reducing latency.
- Qdrant as a vector database for semantic search.
- MinIO for scalable object storage of documents.
- Celery for managing background tasks, ensuring real-time user experience is not impacted by document processing.
This high-level architecture is designed to support a fast, scalable, and cost-effective solution for assisting employees with document-based query responses. It leverages modern microservices architecture principles, providing a robust foundation for further enhancements.